A+ Exam Objective – 1.4 Given a scenario, configure basic mobile-device network connectivity and application support.
Welcome to ExamNotes by CertBlaster! This installment looks at the ports and accessories available on mobile devices. We’ll look at the connection types, the physical connection, and any communication protocols that may be used. Enjoy!
Click here to go back to the Table of Content
Wireless / cellular data network (enable/disable)
Here we will look at a few wireless data device configurations and usages. For this section, consider an anonymous mobile device and service provider. The mobile service plan has unlimited 4G LTE service on calls and data. The unlimited calls and data factor is a consideration when we talk about sharing services. Also, it is a good way to validate access to your service.
Airplane mode
If you suffer a loss of connectivity, first check if that little airplane icon on your smartphone is showing. The first icon on your phone indicates that the device’s radios are capable of communication.

The initial proliferation of cellular and Wi-Fi-capable devices prompted a concern among airlines that these devices could interfere with the safe operation of the systems on an aircraft. Passengers were instructed to turn their devices off. Boring! Device manufacturers came up with a quick mode, called Airplane mode, which disables the offending radios. Pressing the airplane icon switches off all the external communication methods of the device.

Hotspot
In general, the term hotspot refers to an area where you can wirelessly connect to the internet and other application layer services such as email, messaging, and social media. Many businesses, including prominent coffee houses, offer this service as a way to encourage patrons to stay at their location, providing additional sales opportunities that a grab-and-go patron would not be exposed to. Having a delicate, icing drizzled pastry in your field of vision will have an effect on you. It won’t be long before you’re back at the counter either for a refill or that pastry!
Depending on the device’s capabilities, your own wireless device can be turned into a hotspot. With your own hotspot, you can have a completely supported wireless business meeting with a small group at a park or a lake, anywhere but that conference room. In most cases, the device sharing the hotspot will have its internet capability disabled. Bandwidth will not reflect the full capacity of the host and battery life will be impacted.
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) vs. code-division multiple access (CDMA)
Cellular communication takes place over a CDMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access) networks of fixed antennae which are placed strategically to provide the best coverage areas in North America. International satellites, in conjunction with CDMA, are used in the GSM (Global System for Mobile Technology) standard which prevails in the rest of the “covered” world. Cellular service, in any of its varieties (later), is the largest wireless internet connection type in the world.
2G cellular is actually slower than dial-up on paper. Speeds may vary but don’t expect more than 50Kbps on this connection. The next advance was 2G E or 2G EDGE (Enhanced Data for GSM Evolution) which brought the speed up to 384Kbps. Then came 3G which is a noteworthy improvement when properly implemented. Speeds are between 200K and 4Mbps. However, check for the latest revision of the standard. The hands-down winner currently is 4G (LTE or WiMAX) and will get between 100Mbps and 1Gbps. 5G is the fastest you are likely to encounter today. 5G offers speeds up to 20GBps at peak and in some cases can actually be faster than WiFi!
Preferred Roaming List (PRL) updates
PRL Update The PRL is a database file stored in your cellular device. Called the Preferred Roaming List, this file stores the device’s performance carrier preferences regarding connection frequencies and other settings to be used on the connection.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth has been around for some time, but never really realized its potential until mobile devices began using Bluetooth to establish short-range communication between peripherals and other devices. The most significant and potentially lifesaving application of this technology came when Bluetooth was combined with hands-free headsets, enabling hands-free phone conversations. This made driving while talking much safer. This was enhanced when automakers incorporated Bluetooth into the automobile’s features, allowing users to make calls without even looking at the phone. The technology is available in many devices including headphones, keyboards, and even some heart monitors. When two devices are connected together via Bluetooth, they are said to be paired. Up to 7 additional devices can connect, using a master/slave relationship, in a small network called a PAN (Personal Area Network), also referred to as a piconet. Here is an example of a Bluetooth headset waiting to pair and how a one-to-one connection works. The blue light on the left-hand button will light when paired.

Enable Bluetooth
For starters, both devices must be Bluetooth capable and have Bluetooth enabled when initiated. In most cases, the device will actively search for devices to pair.
Enable pairing
The devices must be set (initially) to discover nearby Bluetooth devices. In essence, one device must be discoverable for the other device to find it. Most devices enter this mode for 15 to 30 seconds when powered up. If the devices are set to automatically pair, you’ll be connected after a couple of easy clicks.
Find device for pairing
One of the devices will initiate the paging process that will locate other devices and establish the parameters for the connection. Automatic pairing is not the best practice as it leaves you more susceptible to Bluetooth attacks such as Bluesnarfing and Bluejacking (covered later). Consider the environment you expect to be in and picture a 10-meter range around yourself. Here, in three steps, is a Headset pairing to a PC.
Enter the appropriate pin code
One way to protect your device from unauthorized access is the use of a passcode or PIN. Many devices require this to establish a Bluetooth connection. Your hands-free car setup generally requires this as do most keyboards and other command and control peripherals.
The problem with this is that the passcodes are so simple that they are practically guaranteed to be cracked. For example, you will encounter default codes such as 0000, 1111, or the most secure 1234. Most users don’t even think of changing it. Here’s a Tablet that has a decently complex PIN.
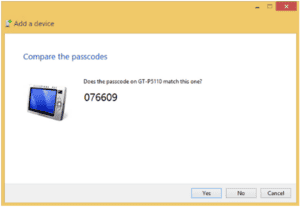
Test connectivity
Testing the connection can be as simple as trying the device. However, depending on your software, there may be in-app connection testing available. In the app, you can see items such as connection speed, signal strength, and signal confirmation which are generally found under Settings/ Bluetooth. 3rd party programs are also available.
Location services
Global Positioning System (GPS) services
The foundation of the Global Positioning System (GPS) consists of satellites which are orbiting the earth in a fixed position relative to the earth’s surface. This orbit is referred to as a geosynchronous orbit. A minimum of three satellites is used by the GPS module inside your personal device to determine the exact location. The time required to receive the signals from the GPS satellites is measured and triangulated to determine your precise location.

Cellular location services
When your location services are active your precise location will be available to any app on your device that has permission. Your Longitude/Latitude coordinates are constantly tracked. Use location services judiciously since you could have background apps tracking your movements. An indication would be a message asking, “How was Joe’s diner?”. You may have been at a traffic signal near Joe’s, but your phone will think you were there. The location data may also be stored with any picture you take.
Mobile device management (MDM)/mobile application management (MAM)
In the corporate environment mobile devices represent several security issues. The issues can be resolved using Mobile Device Management (MDM) to provide or deny network access depending on how the policy is configured. Any apps that require access to network resources will adhere to the company’s Mobile Application Management (MAM) policy. These mobile apps will be considered corporate applications.
Two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication uses two data points to permit access. These could be a password or PIN, an ID badge, your fingerprint or even voice or facial recognition. Both challenges must be met for successful access.
Corporate email configuration
Your corporate email account will be configured by a policy created by your system administrator. It may contain certain restrictions like time of day or geographic limitations.
Mobile device synchronization
Your mobile data can be synchronized to dedicated servers in your business or personal workspace. You can use Google Work Space for business or simply the Chrome Browser in the personal setting.
Recognizing data caps
If you are on a metered connection or connected to your employer’s network, the amount of data you use is tracked. You may receive a warning with your usage and data cap displayed. Based on this information you can adjust your usage, like backups and Synchs to avoid a problem. And, don’t stream movies at work!
– Microsoft 365 organizes your email, contacts, backups and more. It uses data analytics to track your app usage in associated accounts and relevant Microsoft products . You can use it to track performance and time usage. This information can be accessed and reviewed in the Admin Portal.
– ActiveSync was an advanced Microsoft mobile device synchronization app that is depredated for individuals. It was replaced by Windows Mobile Device Center which was ultimately also depredated for data synchronization. Your alternative is use of a 3rd party app or device registry reconfiguration. ActiveSync is still available to Exchange users.
Both Windows and Google provide synchronization apps for your selected data like email, contacts, and calendar. A Google Workspace is used to collect this data and Microsoft 365 does the same and more.
– Commercial mail application
Both Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace Will work efficiently with email, calendar, contacts, tasks, and more.
Well, that’s all for domain 1.4 and Main Domain 1.0. Now it’s on to domain 2.0! Good luck!

