A+ Exam Objective 3.7 Given a scenario, install and replace printer consumables.
Click here to go back to the A+ Main Domain 3.0 Table of Content
Welcome to Exam Notes by CertBlaster! In this article, we will cover Core 1 objective 3.7 Given a scenario, install and replace printer consumables.
Now it’s time to cover one of the most important and exciting topics yet! Printers!! Before we get too deep into it, we will diffuse a potentially volatile topic that will not be appearing on your tests.
We will break down the printers by type and then for each type, we will describe the components and troubleshoot various printer problems, tracing them back to the component that is responsible.
To start we’ll define what most certainly be your primary tasks:
Laser
Replace toner, apply maintenance kit, perform calibration, and clean.
Thermal
Replace paper, clean the heating element, and remove debris.
Impact
Replace ribbon, replace print head, replace paper.
Inkjet
Clean heads, replace cartridges, perform calibration, and clear jams.
Laser Printers

Laser printers basically have two main areas of concern:
- The printer, i.e. everything that is not the toner cartridge.
- The toner cartridge
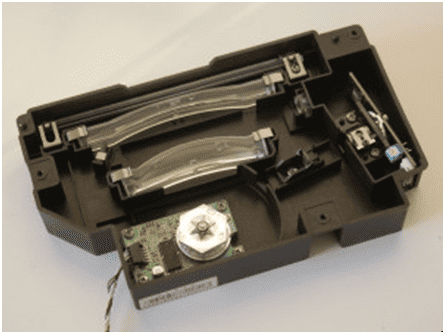
Understanding the printing process step-by-step is your best path to success in this area. All steps are occurring so fast that they appear to happen almost simultaneously. We will look at each step, where it fits in the process, and how it relates to other processes.
The cartridge contains all (or most) of the components needed to create the image and to prepare it for transfer to the page.
Cartridge: This is the main replaceable item in a Laser printer. The cartridge contains the drum, toner hopper, agitator blade, wiper blade, and the shutter. Ever since the replaceable cartridge was introduced to laser printing, maintenance and support needs of these printers have been significantly reduced.

The ink cartridge, the drum, and the toner contain everything that could be considered a consumable or wear item.
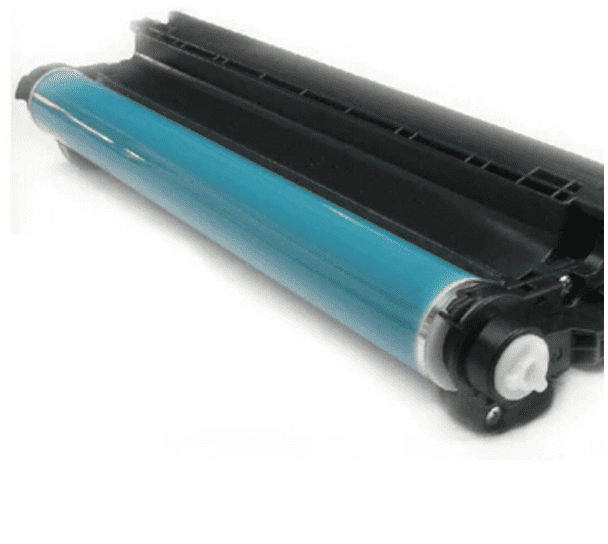

This includes the transfer belt, transfer roller, pickup rollers, separator pads, and duplexing assembly.
Laser printing is a photo-electric process.
Charging: The imaging drum has a very high negative voltage (-600V) applied to it by a roller or a wire depending on the age.
Exposing: In this stage, the laser writes the image onto the drum, increasing the voltage of the exposed areas from approximately -600V to -100V.
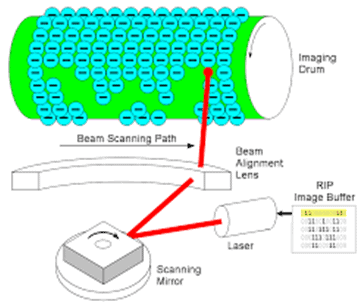
Developing: The toner is applied to the drum by applying a light charge, attracting the toner to the highly charged drum.
Fusing: The fusing assembly provides both friction and heat to the paper as it passes through, melting the toner onto the paper.
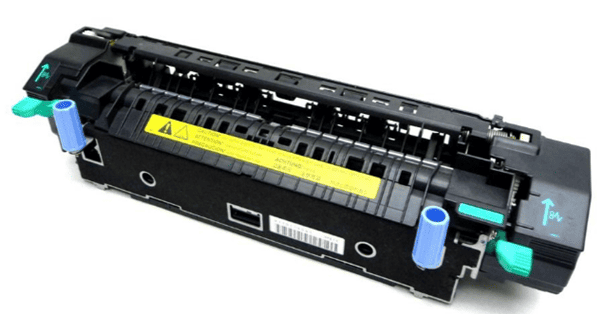
Cleaning: The drum is cleaned so that a new page can be printed. This process utilizes the erase lamps which are a part of the printer lid and are often covered with red film. Exposing the drum to this light erases the drum completely. The scraper blade also removes any remnants, leaving a completely clean drum ready for a new page to print.

Example of preventative maintenance on an HP LaserJet
As part of your periodic maintenance duties, you will be assigned one or two printers to perform preventative maintenance. You have been asked to perform preventative maintenance on an HP LaserJet.

First, use the model number to look up the maintenance schedule for your unit(s). After looking it up, you see the printer needs new rollers, vacuuming, and toner cartridge replacement. In your toolkit, you have a Datavac/2 Pro Series Toner Vac because it meets HP’s stringent requirements, along with many other manufacturers. New printer parts are approved when they pass the manufacturer’s requirements and are guaranteed to fit.

An additional part that is becoming more popular in new printers is the transfer belt or roller. This is used to move documents through multicolor laser printers and scanners. Having the right tools and documentation are crucial aspects when working on this.
Inkjet
Now to the bread and butter of SOHO printer implementations, we have InkJet printers. These are an inexpensive and economical addition to your Small/Home Office that will give your mailings, business cards, and pictures that extra pop! You can use them to print decent letters too!
Whatever your design of choice, you will find inkjet printers that are available in every price range and feature configuration. Inkjets are compatible with most OSs and connection types.
Ink cartridges are modular and can be replaced one at a time, reducing the general maintenance cost. Each cartridge uses a heated nozzle to dispense precise amounts of ink in order to produce the desired color or pattern. The colored ink modules are driven back and forth on each line in order to produce continuous, seamless, and high-resolution output. Many models use belt-driven ink delivery. These machines have evolved from cheap laser alternatives into full-fledged, multifunction devices incorporating scanners, copiers, and fax machines that can also act as standalone wireless devices. With the addition of a duplexer, this modest little printer can play with the big boys!
Whenever you change a printer cartridge, the machine must be recalibrated. If calibration is not performed, your print quality will suffer.
Thermal After having paid for something at a cash register, have you ever looked at your receipt and wondered why it looks funny and old-school and why there are two? This is a thermal receipt and is one of the oldest cash accounting printing technologies still in use.
Impact Printing, or Dot Matrix, was developed concurrently with thermal. As money became more valuable, the desire to pilfer even small amounts grew quickly. With no tracking system, companies could literally be robbed out of solvency by their own employees. Adding machines were created to generate a hard copy of any tabulations and to generate a record of all transactions. The current benefit of the dot matrix is its ability to print out multiple copies of the same document, known as carbon copies.
Dot Matrix technology uses a ribbon that is impregnated with ink and a set of pins that fire independently, transferring a dot of ink on the paper at the point of impact. This point of impact has sufficient force to activate the carbon in a multi-page document so that duplicates can be generated in real-time.
Virtual
Every computer in the world has the opportunity to create a virtual counterpart. For the 220-1101 3.7 sub-objective, you are expected to know specifically that you can use your Operating System (OS) tools to perform the following actions:
Print to file: The default output saved from Print-to-file is a .prn file. Check the Print-to-file box in the Printer Properties applet.
Print to PDF: Check the Print-to-PDF box in the Printer Properties applet.
Print to XPS: Checking this uses the built-in Microsoft printer.
Print to image: Installing PDFill (a 3rd party program) will allow the Microsoft printer to print directly to an image format such as PNG, PPG, BMP, TIF or GIF.
3D Printers
Plastic filament
The prices for 3D printers, in addition to the materials used to print 3D objects, are beginning to drop. Once costing tens of thousands of dollars, 3D printers can now be purchased for a thousand dollars. Printing materials have become more affordable, with materials such as plastic filament now costing around twenty dollars or less. That’s cheaper than inkjet cartridges! The filament will come on spools.
3.7 Resin Printing
3D resin can also be used for 3D printing. 3D resin comes in a tank.
Print Bed Both of the methods described deposit the print project on a print bed. It is important that the print bed be flat, level, and stable.
During the 3D printing process, software is needed to create the 3D model and transfer the model to the 3D printer. The object can then be printed in pretty much the same way as with a standard printer.
During standard 2D paper printing, a horizontal 1D stripe is deposited line-by-line until the image or text is complete. With 3D printing, each pass of the printer head creates fine layers of the chosen material, in our case plastic filament, that stack vertically. This process is called Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) or Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). Both of these processes are additive, meaning that each print layer is added on top of the object until the object is complete. Depending on the process, the filament is melted with UV light or heat.
That’s all for objective 3.7 and for main domain 3. You’re over halfway there! Good luck with the test!
Click here to go back to the A+ Main Domain 3.0 Table of Content

