Welcome to Exam Notes by CertBlaster! This edition covers Network+ Sub-domain 2.2: The placement and configuration of network devices. Enjoy!
A hub is a multiport repeater that sends the data received on one port and sends it to all other ports on the device. This is acceptable on small networks but as networks grew the increased traffic was sent to all ports and prone to collisions A hub operates in half-duplex mode meaning it can not send and receive data simultaneously. Hubs are virtually obsolete largely due to the low cost and improved performance of switches.

Hub
A bridge is a Layer 2 device that can be used to connect dissimilar network topologies like wireless to Ethernet. or to segment a large network into smaller ones to reduce traffic and collisions. The bridge uses MAC addresses and software to direct network traffic. A bridge is a Layer 2 device.
A switch is a Layer 2 device that can eliminate collisions and speed up traffic. Switches operate in full duplex mode allowing simultaneous send and receive capabilities between each port. In contrast to a hub that transmits data to all ports. The switch uses the Layer 2 MAC address to send the data to only the intended recipients. You may see a switch referred to as a MAC Bridge. There are more switch features that we will look at in the next edition.

Switch
A router uses IP addresses to direct traffic. When configured properly it can manage traffic between subnets and VLANs. Routers are the backbone of the internet. They can quickly determine the best path between two points and reroute traffic around device failures or congestion. Routers can be configured to permit or deny communication based on the protocol used, IP addressing and port number. Routers use Access Control Lists (ACL)to define traffic behavior.
Modems perform the function of translating a signal from different formats. We call this process modulation when we are transmitting and demodulation when receiving the signals MODEM for short The most recognizable example is the Phone modem that takes the audio analog signal sent across a connection using the Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) connection and converts (demodulates) it to a digital signal for the PC. The PCs digital response is then modulated to analog for transmission. It is quite common to see cable modems in many networks. The cable modem converts the digital signal from the provider and converts it to Ethernet or wireless signals making it more of a bridge than a modem.
A firewall can be a hardware device or software. The hardware device is called a network-based firewall. Firewall software installed on individual devices is called a host-based firewall In a network diagram, the firewall is shown as a device and looks like a brick wall. A standard firewall filters traffic based on the Layer 4 Port and protocol (packet filter). There should always be a firewall between your private network and the internet.
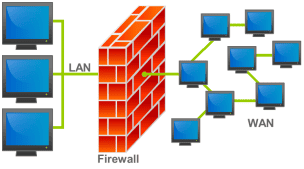
Firewall
A wireless access point (WAP) is capable of receiving wireless signals from multiple nodes and then retransmitting them within its coverage area. It is important that the WAPs are placed effectively and have enough power to perform their function.
Operating at OSI Layer 1 a media converter enables you to take advantage of the optimal network media to meet your needs. For example, if you need a connection that exceeds the 100m Ethernet limitation you can switch from copper to fiberoptic media on one end and then back to copper using another media converter if necessary.
A wireless range extender works by repeating all wireless signals, thereby extending the effective range of wireless transmissions. These are common in home deployments where the signal does not cover the entire living area. The wireless range extender can be placed strategically to provide the necessary coverage.
The VoIP endpoint is the device that receives VoIP traffic intended for it. The devices here cover a wide range and include IoT devices. Here we will define PCs with VoIP capabilities and mobile devices like cell phones and enabled tablets. The most common implementation is VoIP telephones.
That’s all for 2.2! See you at 2.3! Good luck on the test!

By continuing to browse this site, you accept the use of cookies and similar technologies that will allow the use of your data by CertBlaster in order to produce audience statistics- see our privacy policy.